What Health Complications can Crohn’s Disease Cause
Crohn’s Disease
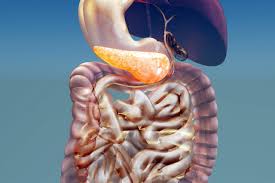
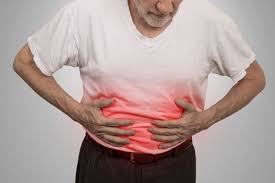
A form of inflammatory digestive disease (IBD) known as Crohn’s disease causes the digestion to get irritated and swelling. If you suffer from Crohn’s disease it is possible that you will be suffering from abdominal pain, diarrhea, rectal bleeding, and weight loss. It is a chronic condition which cannot be treated. However, treatments for Crohn’s disease generally manage the symptoms and enable you to lead a full life.
Types of Crohn’s disease
There exist five kinds of Crohn’s Disease. Each is a separate area within the GI tract:
- Ileocolitis
- Ileitis
- Gastroduodenal Crohn’s Disease
- Jejunoileitis
- Crohn’s Colitis
Complications of the Crohn’s Disease
There’s no cure or cure for Crohn’s disease, but you can manage your symptoms and enter the remission phase with effective treatment. If you don’t treat Crohn’s, it can allow the disease to worsen, and can lead to serious complications.
To be successful Your treatment for Crohn’s disease should be continuous. It’s crucial to follow healthy eating habits and to continue using your medication even if you’re feeling better.
Here are a few complications that can arise from untreated Crohn’s Disease:
- Intestinal obstruction
Crohn’s disease may cause thickening of the walls in the intestinal tract. As time passes the thickened regions of your intestines could become narrow and cause obstruction to the digestive tract. A complete or partial digestive obstruction also known as an bowel obstruction, can impede the flow of food or stool through your intestinal tract.
- Stricture
A stricture refers to an intestinal narrowing due to chronic inflammation.
- Abscesses and fistulas
Ulcers that completely penetrate the wall of the digestive tract can produce fistulas. They are abnormal connections that connect the intestines to different organs.
Around one in three people who suffer from Crohn’s disease be diagnosed with fistula.
A fistula that is located in the abdomen can cause food to be pushed out of important bowel spaces that are required to absorb food. Fistulas can also form from the bowel into the bladder vagina, skin, or bowel and drain the contents of the bowel to these regions.
If untreated the fistula that is infected could develop into a potentially life-threatening abscess.
To avoid a serious infection fistulas need to be treated promptly. Treatment options are surgery, medication or a combination of both.
- Malnutrition
Some of the problems associated with malnutrition are:
- Diarrhoea can cause the body to lose fluids, which could lead to dehydration. Severe dehydration can damage your kidneys.
- Anaemia – a decrease in iron levels in the diet and loss of blood from the bowel can cause anaemia (the blood is not carrying sufficient oxygen).
- Reduced appetite and inadequate absorption of nutrients in food can lead to weight loss.
- Growth is slowed (in children) Inadequate nutrition in early childhood and into adolescence may hinder the growth of a child and their physical development.
- Ulcers
Ulcers are open sores which can develop anywhere in the digestive tract can be seen in people suffering from Crohn’s disease.
They can be dangerous and painful when they result in internal bleeding. They may also cause perforations, or holes within the digestive tract. This can let digestive contents be absorbed into the abdomen.
If this happens, prompt medical attention is needed.
- Toxic megacolon
Toxic megacolon is a very rare complications. The slight abdominal ditension (bloating) is normal and non-injurious, even in those who do not have IBD. However the inflamed and red the large the intestine (large the bowel) of an individual suffering from IBD can suddenly and terribly dilate. The intestinal wall could expand to the point that it bursts (bursts). The bowel that ruptures discharges their contents onto the stomach cavity which can cause inflammation (peritonitis).
- Others
Crohn’s disease may cause range of inflammatory conditions beyond digestion. The most common sites are joint, skin and mouths the eyes and liver, and the bile drainage channels.
How do I treat for Crohn’s Disease?
Medical Treatment for Crohn’s Disease
There is no cure currently for Crohn’s disease and there isn’t any one treatment that is suitable for all. The aim of treatment is to lessen the symptoms.
Your physician can prescribe anti-inflammatory medicines such as immune system suppressors, medications for pain relief as well as antidiarrheal supplements. In the case of severe illness, the doctor could prescribe nutrition therapy (wherein the diet is prescribed through a feeding tube or nutrients injected into veins to treat your Crohn’s condition) or surgical procedures.